
The adoption of smart metering in minigrids is playing a crucial role in addressing electricity shortages in remote areas of Africa. Minigrids are small, independent power systems that typically rely on solar, wind, or hybrid energy sources, combined with battery storage and backup diesel generators, to meet the electricity needs of local communities and businesses. Smart meters are essential in these systems as they enable remote monitoring, efficient power management, and tiered billing, particularly supporting prepaid and pay-as-you-go (PAYG) models. These models allow users to purchase electricity flexibly through mobile payment platforms such as M-Pesa and MTN Mobile Money, improving accessibility while reducing operational costs for utility providers. The African minigrid market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by investments from international organizations such as the World Bank and the African Development Bank, as well as private sector players like Azuri Technologies, Engie Energy Access, and Zola Electric. However, challenges remain, including high initial investment costs, difficulties in infrastructure maintenance, and regulatory uncertainties across different countries. As technology advances and financial support increases, smart metering in minigrids is expected to scale further, bringing reliable electricity to millions of people who currently lack access.
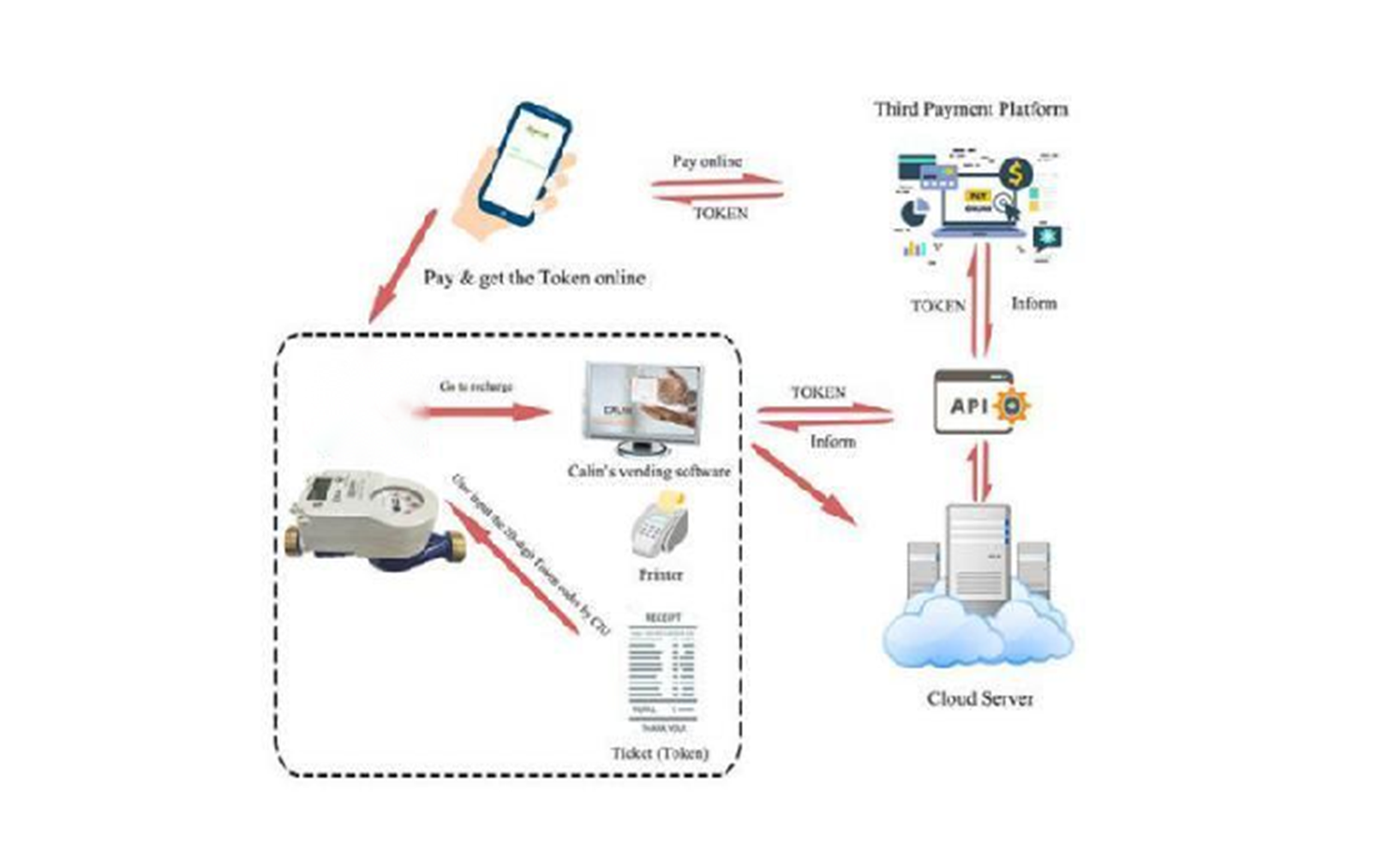
The LoRaWAN centralized meter reading solution offers key advantages for smart water meters. Utilizing Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology, it enables long-range data transmission with minimal power consumption, extending battery life to 8-10 years and reducing maintenance costs.
LoRaWAN ensures stable communication even in challenging environments like underground pits, dense urban areas, or remote locations, thanks to its strong anti-interference capabilities and excellent signal penetration. This enhances the accuracy and reliability of meter readings.
The solution supports large-scale deployments, managing thousands of water meters simultaneously. This is ideal for municipal utilities, residential communities, and industrial parks, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs. Additionally, integration with cloud platforms allows remote monitoring, data analysis, and leakage detection, optimizing water management and reducing waste.
Overall, the LoRaWAN solution provides an efficient, cost-effective, and scalable approach to smart water management, contributing to the development of smart cities.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) modernizes urban energy systems by integrating smart meters and data-driven communication networks. Tailored for cities, it enables real-time energy monitoring, accurate billing, and efficient grid management, supporting sustainability goals.
AMI employs smart meters to collect granular consumption data, transmitted via cellular or LPWAN networks to utility platforms. This bidirectional connectivity enables utilities to monitor usage, detect faults remotely, and implement dynamic pricing. Consumers gain real-time insights via digital portals to optimize consumption.
For urban grids, AMI enhances reliability by balancing demand during peak periods and enabling rapid outage resolution. It seamlessly integrates renewables and EV infrastructure, accelerating clean energy transitions. By automating meter readings, AMI cuts operational costs and human error, while its analytics aid infrastructure planning and regulatory compliance.
As a cornerstone of smart cities, AMI drives energy conservation, reduces emissions, and fosters resilient urban energy networks, aligning with global sustainability agendas.
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.